pytorch学习(2)——Dataset类使用、图像数据集调用
pytorch数据集调用
1 函数
1.1 dir()函数
函数功能:打开包。
在pycharm 的python console中输入:
In[1]: import torch
In[2]: dir(torch)
Out[2]: ......
In[3]: dir(torch.cuda)
Out[3]: ......
In[4]: dir(torch.cuda.is_available)
Out[4]:
['__annotations__',
'__call__',
'__class__',
'__closure__',
'__code__',
'__defaults__',
'__delattr__',
'__dict__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__get__',
'__getattribute__',
'__globals__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__kwdefaults__',
'__le__',
'__lt__',
'__module__',
'__name__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__qualname__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__']
help(torch.cuda.is_available)
Help on function is_available in module torch.cuda:
is_available() -> bool
Returns a bool indicating if CUDA is currently available.
可以观察到不同的输出。
有__init__双下划线表示约定好不可修改的函数。
1.2 help()函数
函数功能:输出函数的功能细节。
在pycharm 的python console中输入:
In[5]: help(torch.cuda.is_available)
Out[5]:
Help on function is_available in module torch.cuda:
is_available() -> bool
Returns a bool indicating if CUDA is currently available.
2 输出Hello world
2.1 pycharm新建文件
新建.py文件,输入:print("hello world")。右键运行。

2.2 Python Console
输入:print("hello world"),回车。

2.3 jupyter
打开Conda Prompt,输入:
(base) C:\Users\win10>conda activate pytorch
(pytorch) C:\Users\win10>jupyter notebook
打开jupyter,输入:print("hello world"),点击运行,或者使用快捷键:Shift+回车。

2.4 三者的区别
1、python文件以整个文件(所有行)为块,每次都是从头执行。优点:通用,传播方便,适用于大型项目。缺点:只能从头运行。
2、python Console以单独的行为块,从新执行会从错误处开始。优点:显示每个变量的值,调试功能。缺点:不利于代码阅读及修改。
3、jupyter以任意行为块运行的,运行到错误的地方之前都是一整块,错误改正之后,也是一整块运行。优点:利于代码阅读和修改。缺点:环境需要配置。
3 PyTorch加载数据
3.1 Dataset类
作用:提供一种方式去获取数据及其label。
(1)如何获取每一个数据以及label。
(2)告诉我们总共有多少的数据。
3.2 Dataloader
作用:为网络提供不同的数据形式。
3.3 下载数据集
区别蚂蚁和蜜蜂的图像,下载链接:https://download.pytorch.org/tutorial/hymenoptera_data.zip
文件结构:
- dataset
- train
- ants
- bees
- val
- ants
- bees
需要修改文件结构:
新文件结构:
- dataset_ants_bees
- train
- ants_image(ants修改)
- ants_label(新建)
- bees_image(bees修改)
- bees_image(新建)
- val
- ants
- bees
3.4 使用Dataset类
jupyter输入。
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
help(Dataset)
Help on class Dataset in module torch.utils.data.dataset:
class Dataset(typing.Generic)
| An abstract class representing a :class:`Dataset`.
|
| All datasets that represent a map from keys to data samples should subclass
| it. All subclasses should overwrite :meth:`__getitem__`, supporting fetching a
| data sample for a given key. Subclasses could also optionally overwrite
| :meth:`__len__`, which is expected to return the size of the dataset by many
| :class:`~torch.utils.data.Sampler` implementations and the default options
| of :class:`~torch.utils.data.DataLoader`.
|
| .. note::
| :class:`~torch.utils.data.DataLoader` by default constructs a index
| sampler that yields integral indices. To make it work with a map-style
| dataset with non-integral indices/keys, a custom sampler must be provided.
|
| Method resolution order:
| Dataset
| typing.Generic
| builtins.object
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __add__(self, other: 'Dataset[T_co]') -> 'ConcatDataset[T_co]'
|
| __getitem__(self, index) -> +T_co
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| __orig_bases__ = (typing.Generic[+T_co],)
|
| __parameters__ = (+T_co,)
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from typing.Generic:
|
| __class_getitem__(params) from builtins.type
|
| __init_subclass__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| This method is called when a class is subclassed.
|
| The default implementation does nothing. It may be
| overridden to extend subclasses.
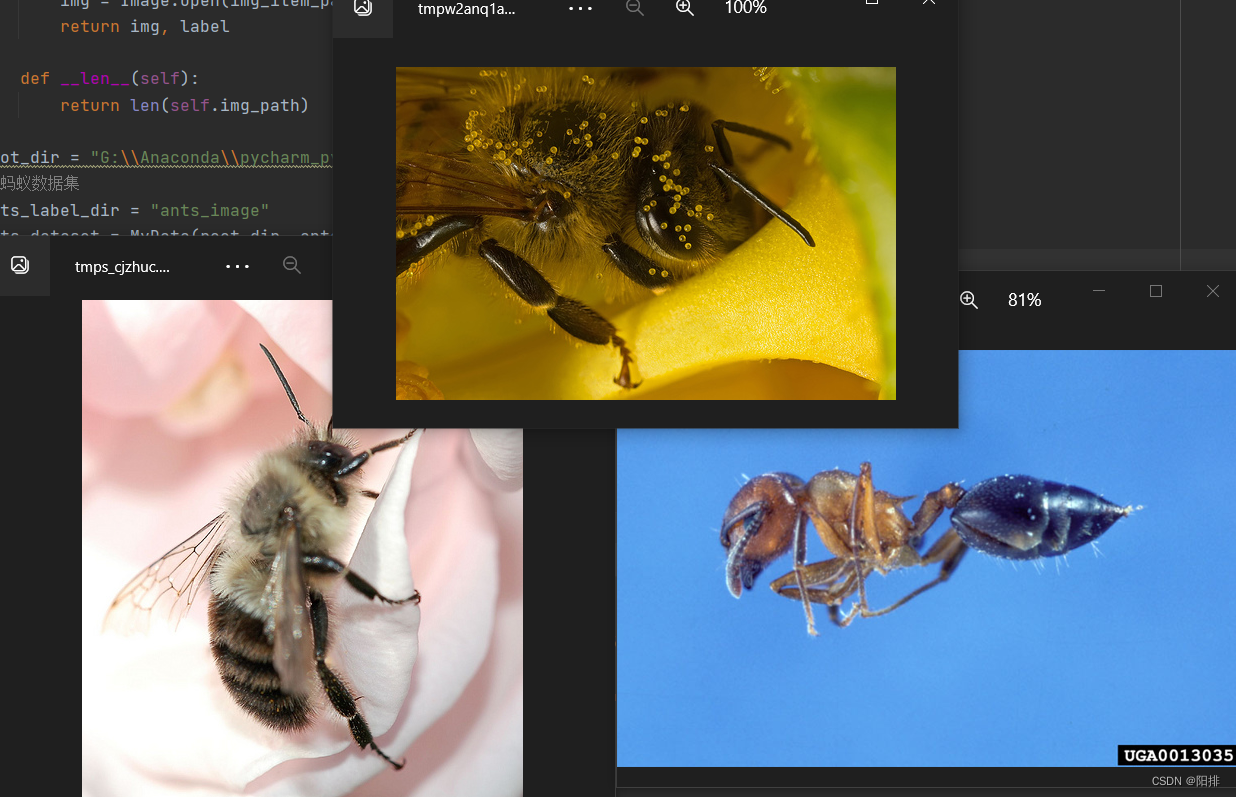
3.5 读取数据集并显示图像
编写python脚本,定义MyData类继承于DataSet类,定义__init__、__getitem__、__len__函数,并调用函数,显示图像。
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from PIL import Image
import os
class MyData(Dataset):
def __init__(self,root_dir,label_dir):
self.root_dir = root_dir # 根目录路径
self.label_dir = label_dir # 标签目录路径
self.path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir) # 合成成总路径
print("path: ", self.path)
self.img_path = os.listdir(self.path) # 获取所有图片的地址
print("img_path: ", self.img_path)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_name = self.img_path[idx]
img_item_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir, img_name)
label = self.label_dir
img = Image.open(img_item_path)
return img, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_path)
root_dir = "G:\\Anaconda\\pycharm_pytorch\\learning_project\\dataset_ants_bees\\train"
# 蚂蚁数据集
ants_label_dir = "ants_image"
ants_dataset = MyData(root_dir, ants_label_dir)
img_ants, label_ants = ants_dataset[0]
img_ants.show()
# 蜜蜂数据集
bees_label_dir = "bees_image"
bees_dataset = MyData(root_dir, bees_label_dir)
img_bees, label_bees = bees_dataset[0]
img_bees.show()
# 合并数据集
train_dataset = ants_dataset + bees_dataset
len(train_dataset)
len(ants_dataset)
len(bees_dataset)
img_train, label = train_dataset[200]
img_train.show()

3.6 添加标签
因为之前下载的数据集只有图像,没有每个图像对应的标签,因此自己写一个自动生成标签的python脚本:
# 程序功能:生成train文件夹下XXXX_label文件夹下的.txt文件和其标签内容,对应于XXXX_image文件夹下的图片名称
import os
root_dir = "G:\\Anaconda\\pycharm_pytorch\\learning_project\\dataset_ants_bees\\train"
image_dir = ["bees_image", "ants_image"] # 标签目录路径
label_dir = ["bees_label", "ants_label"] # 标签目录路径
label = ["bee","ant"]
for i in range(2):
path_image = os.path.join(root_dir, image_dir[i]) # 合成图像总路径
path_label = os.path.join(root_dir, label_dir[i]) # 合成标签总路径
img_path = os.listdir(path_image) # 获取所有图片的地址
for idx in range(len(img_path)):
file_name = img_path[idx][:-4] + ".txt"
file_path = os.path.join(path_label, file_name)
print(file_path)
file = open(file_path, "w", encoding='utf-8')
file.write(label[i])
file.close()
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容






所有评论(0)